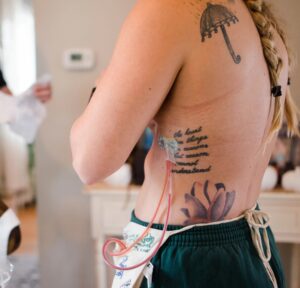By Iris Farrou
17 Oct, 2023
Diet & Exercise, Lifestyle Tips, Prevention, Procedures, Women's Health
Bone Density, Bone Mass, DEXA, does calcium prevent osteoporosis, How to prevent onset of osteoporosis, Mineral Density, Osteoporosis, Prevention, Scan, Test, what is a DEXA scan, X-Ray
 If you have a family history of osteoporosis or are postmenopausal and suspect osteoporosis will affect your quality of life, then it may be time to take a closer look at what this “silent disease” i, how you can prevent it from taking control of your life, and the medical technology available to help you know your body.
If you have a family history of osteoporosis or are postmenopausal and suspect osteoporosis will affect your quality of life, then it may be time to take a closer look at what this “silent disease” i, how you can prevent it from taking control of your life, and the medical technology available to help you know your body.
Very simply, osteoporosis means that your bone mass and mineral density have decreased, thus diminishing the strength of your bones and increasing the risk of fractures. Although many believe only women are at risk for osteoporosis, that is not true: this disease affects men as well, and all genders as we get older. The first step to determining whether you have osteoporosis is a physical exam:
- Loss of height and weight may be signs of osteoporosis, as well as changes in posture
- If you’ve had a fracture that has not healed this is also a big sign of osteoporosis
- Balance and the way you walk can be affected by osteoporosis too
If the physical exam, along with your medical history and age, determines you may have osteoporosis then your doctor will order an exam to measure your bone density. This is where DEXA tests come in, which measure the mineral content of your bones, focusing on certain areas of your skeleton. DEXA stands for “dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry” and it is a medical imaging test; it uses very low levels of x-ray to determine how dense your bones may be (or not be).
What does the test involve?
Although it is a test you may not want to pass, medical professionals consider DEXA scans to be one of the most effective, quick and painless, as well as useful ways to diagnose osteoporosis.
- You will lie on the special DEXA x-ray table and the technologists will help you hold the desired position by using positioning devices.
- The arm of the DEXA machine will pass over your body, and two different x-ray beams with miniscule radiation distinguish bone from other tissue.
- The scanner gathers the data and translates the bone density information into pictures and graphs.
- A radiologist or other physician that has been trained in DEXA interpretation reviews and interprets the results of the scan. The expert sends a report to your primary doctor, who in turn discusses the results with you and determines the appropriate treatment.
Why is DEXA more effective than other methods?
As you may know, there are other body imaging methods that medical providers use: if you have a broken bone, you will most likely get an X-ray done, while if you experience constant headaches your doctor may order an MRI. DEXA very specifically measures bone density, and it also measures bone density in each specific area of the body. A common misconception is that our bone density is the same throughout our skeletal system, but DEXA is able to determine lean skeletal, fat, and bone masses in various spots in our body.
More
By Iris Farrou
30 Sep, 2023
Breast Cancer, Breast health, Lifestyle Tips, Prevention, Procedures, Queer Health, Women's Health
boob job, breast, breast augmentation, Breast cancer, breast lift, chest masculinization, cosmetic, gender affirming surgery, how to fix breast shape, implants, lumpectomy, male breast cancer, male breast reduction, mastectomy, men with breast cancer, partial, reconstruction, reduction, remove implants, surgery, top surgery
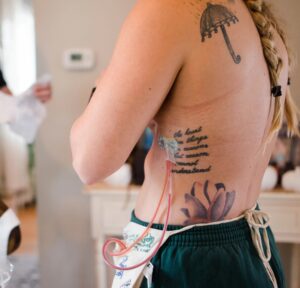
The conversation around breast reconstruction surgeries focuses on women who have had either a mastectomy or a lumpectomy done and wish to reconstruct their breasts once they are cancer free. This is a wonderful opportunity for women who are cancer survivors, and of course, a very body-affirming procedure as well! According to 2020 data from the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, breast augmentation surgery has been in the top 5 cosmetic surgeries since 2006, followed by breast implant removals, lifts, and reductions. The highest demographic for breast procedures are women ages 40-54. Sometimes, breast reconstruction surgeries get categorized alongside cosmetic breast procedures. Though there is definitely an overlap, these are the most common breast surgeries:
- Breast augmentation that increases the size of the breasts and may affect the shape and cleavage as well.
- Breast lift, which tightens the existing tissue for a more refined breast shape.
- A combination of breast augmentation with lift, for a one-time makeover.
- Breast revision: patients update their existing implants, can change the size or shape of their breasts, or completely remove the implants.
- Breast reduction for women with excessively large breasts that affect either their body image, create physical problems, or both.
- Male breast reduction for men with excess fat and glandular tissue on their breasts.
All of these procedures reconstruct the breasts in one way or another, and the reasons are often both cosmetic and medical, as well as mental health reasons. A prime example of this is gender affirming top surgery for trans people: either chest feminization or chest masculinization. For chest feminization, surgeons will usually recommend breast augmentation with implants or fat grafting, or a combination. When it comes to chest masculinization, surgeons perform a type of mastectomy that removes breast tissue, eliminates the crease on the bottom of the breast, and reconstructs the nipples according to the patient’s preferences.
Women who have undergone double or partial mastectomy, or a lumpectomy, may choose to have breast reconstruction surgery. Patients whose breast cancer can be removed with surgery have more options on the type of surgery they get done–and can usually have immediate reconstruction surgery right after their breast cancer surgery. However, for medical and/or personal reasons, women can also choose to have delayed reconstruction surgery: months or even years later. There are two main types of post-cancer breast reconstruction surgery:
- Flap Reconstruction: this surgery uses tissue from your own body to form one or both breasts. There are several types of flaps, and the choice is made on a case by case basis. Your surgeon will consider which type is appropriate for you, and whether you safely qualify for this type.
- Implant Reconstruction: much like the cosmetic procedure, silicone or saline implants are used to reconstruct the breast tissue. Your surgeon will either lift the chest muscle and place the implant underneath, or they may place the implant above the chest muscle if they can.
Since every body and case is different, not all options may be available. Whether for medical or cosmetic reasons, consult with your surgeon about your breast surgery options, get several opinions if you can, and see if you are eligible for insurance coverage. Keep in mind some procedures may take a long time to be completed, may need to successfully happen over a period of months, or be regularly maintained to ensure your health and safety.
More
By Iris Farrou
24 Sep, 2023
Lifestyle Tips, Menopause, Mental Health, Peri-Menopause, Queer Health, Reproductive health, Sexual health, Women's Health
Anxiety, asexual, asexuality, assault, boyfriend, Buffalo NY, Depression, exhaustion, fear of intimacy, fiancé, girlfriend, how to be a supportive partner, how to bring up low sex drive, husband, intimacy fears, lack of intimacy, Low libido, low sex drive, medications that kill sex drive, meds, mental health interfere with sex drive, OB/GYN, OBGYN, overwhelmed, partner, PTSD, sexual trauma, talk to my doctor about low libido, what is a healthy sex life, why does my partner not want to have sex, why is my libido gone, wife

This may be a touchy subject for many women, as on the one hand a lot of us experience low sex drive, but on the other hand we don’t talk about it! The issue becomes more complicated when healthcare providers don’t even ask us about our libido, yet hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) is quite a common issue women deal with. Additionally, many psychologists, primary healthcare providers and OBGYNs are trained to care for and treat HSDD. HSDD is defined as the absence of desire for sexual activity and/or sexual fantasies– we most often just refer to it as “low libido,” and like anything else, it can have its ebbs and flows. Lack of sex drive can be frustrating in a relationship, but it is a normal thing to be experiencing, it can be traced back to causes, and it doesn’t mean that it’s permanent or that you do not love or are attracted to your partner.
What Causes It?
Especially in women, low libido can be attributed to hormonal changes or imbalances: this can be during the menstrual cycle as estrogen and progesterone levels rise and lower, during menopause when our estrogen levels dramatically drop, in the case of a total hysterectomy, during pregnancy, or if you have PCOS–just to name a few examples.
Another common reason for low libido in women are mental health issues, as well as medications. Depression and anxiety, PTSD, and past sexual trauma can negatively affect a woman’s desire for sex. Many times, the medications used to treat mental health issues can worsen an already low libido. This does not mean an important medication should be stopped, but you can–and should–bring it up with your therapist or mental healthcare professional.
Life stressors, chronic stress, and fatigue can minimize the body’s natural sexual urges. This is even more prevalent in new mothers, or families with young kids: the everyday exhaustion, lack of sleep, and constant worry simply leave no room for sexual intimacy, or desire thereof.
What Can We Do?
If one partner has low or no interest in sex while in a healthy relationship, remember it is a team effort: it is not up to the partner who has low libido to “solve” the issue and magically become better.
- The first thing to consider and talk about, even if it’s uncomfortable, is relationship issues. Your partner’s desire for sex, or how safe they feel, may be affected by something in the relationship neither of you knew was an issue until you really examined it and talked about it.
- If you and/or your partner face mental health issues, it is important to carefully consider how those may be affecting your sex life. Especially if you take any medications, look into the side effects and talk with your therapists about how they could be affecting your sex drive, and solutions to balance that out.
- Redefine intimacy in ways that work for you, and where sex is not the goal or the starting point. You may plan a romantic date, do small daily things to lessen stress, or start with small affectionate gestures to help strengthen your romantic bond.
If you feel that your lack of interest in sex is related to a more serious health issue, either physical or mental, or to a serious issue in your relationship that you have not communicated about, it may be a good idea to seek out professional help and support. HSDD is not uncommon, and many medical professionals can assist you with it; you know your body and life circumstances best, and with a bit of assistance you will be able to get to the root of the issue much more effectively.
More
By Iris Farrou
18 Sep, 2023
Diet & Exercise, Lifestyle Tips, Mental Health, Prevention, Queer Health, Reproductive health, Sexual health, Women's Health, Young adults & teens
Bisexual, Buffalo NY, Gay, Gender Identity, gender non-conforming, healthcare, How do I find a gynecologist if I'm LGBTQ, How do I find an LGBTQ doctor, Inclusive OBGYN Care, Lesbian, LGBTQIA+, Non-Binary, OBGYN for queer couples, Queer Friendly Doctor, queer health, Queer-Friendly OBGYN, sexual orientation, Transgender

If you belong in the LGBTQ community, you probably know that coming out is constant and not a “rip off the bandaid processm,” as it happens every time you meet someone new. Seeking a medical provider, and specifically an OBGYN, as a queer person can be challenging; if you already have a provider but have not discussed your sexual orientation or gender identity with them, it may be time to prepare for a coming out discussion.
Why does it matter?
It’s understandable you may want to avoid another discussion about your sexual orientation and/or gender identity, but when it comes to healthcare this is vital information so you can get the best possible healthcare. A queer ally doctor would be knowledgeable on the health risks a queer person faces. If you are seeing an OBGYN, being open with them about your sexual orientation is important in getting the care you deserve: proper exams and vaccinations, contraceptive methods (if needed), safe sex and risk factors education, and other preventative care. For example, if you are a lesbian couple trying to conceive, your OBGYN should be your strongest advocate in this process. If you are transitioning, your OBGYN should oversee your hormone intake and be there for you through your hormone replacement therapy, helping you remain healthy both physically and mentally.
How to Find a Queer-Friendly Provider
Whether you are considering coming out to your current doctor or looking for one, it’s good to look for queer friendly signs in a practice: you can inquire whether they have LGBTQ+ patients, or if there are doctors who focus on queer health and are more knowledgeable and experienced. You can also ask for referrals through your community: especially when it comes to finding an OBGYN, word of mouth and personal credibility go a long way. If you are nervous about your initial appointment you can ask a friend or trusted family member to come with you. Sometimes you can also authorize your partner or spouse to speak with your doctor on your behalf about certain matters–should you feel comfortable doing so–or be with you during the appointments.
What Should Providers Do?
Don’t think this should be a one-way street: not all falls on you when you want to ensure a practice is queer friendly. Providers can specifically showcase they are LGBTQ friendly, and a safe space, by doing some of the following:
- Displaying equality symbols in their office and/ or website
- Specifically stating they are knowledgeable about the LGBTQ community and are allies
- Have a visible non-discrimination statement
- Customize their patient intake forms to be appropriately inclusive
Meet the Standards of Practice: a set of recommendations created by the Massachusetts Department of Public Health to improve LGBTQ access to quality care
More
By Iris Farrou
14 Sep, 2023
Fatherhood, Lifestyle Tips, New Moms, Postpartum, Pregnancy, Queer Health, Reproductive health, Sexual health, Women's Health
After Giving Birth, Decreased Sex Drive after Pregnancy, hormone changes, Intimacy, Libido, los sex drive, no interest in sex, post pregnancy, postpartum, Postpartum depression, Sex after giving birth, Why is my sex drive gone, will my libido ever return

When we become pregnant, we anticipate changes in our bodies. We may also have worries about how we will look and feel different after giving birth. Many women are concerned about the changes delivery and a newborn baby creates in their intimate relationships– and who wouldn’t worry about such a profound issue? A baby changes everything, bedroom adventures included!
Medical professionals recommend that you allow your body approximately 4-6 weeks to heal after giving birth: if you have had a C-section, the area will need extra care, so sex may prove a little challenging. During delivery, it is also possible you have had a vaginal tear that needs to heal, or have received an incision to enlarge the vaginal opening. Give your body the time it needs to heal; there is no need to rush.
New mothers experience their body differently after giving birth. Some women feel like their libido may never come back, while others find themselves aroused– a lot of hormones and the release of oxytocin make for a variety of responses to sexual desire; any way you feel is completely normal. There is no right or wrong way to feel or not feel sexual desire and no right or wrong way to listen to your body. To ensure your safety, note that the risk for postpartum complications is highest two weeks after giving birth, regardless of the delivery method. You may also have vaginal discharge during this time, vaginal dryness, general discomfort, or even pain. Fatigue, exhaustion, and lack of sleep are also very common and it is understandable that you may have zero interest in sex while trying to recover and care for your newborn baby.
If and when you and your partner decide to have sex make sure you are completely comfortable and not just trying to get things “back to normal.” Couples go through several changes when their baby is born, and nobody is under any obligation to put their health on the line—especially not a new mother. So, when the time is right for you, keep in mind you may experience some pain during vaginal sex.
Since sex after delivery is guaranteed to be different, consider the following as ways to rebuild your intimacy with your partner and be safe:
- Sex is the end point, not the start. Start small, like hand holding or cuddling.
- Be comfortable: you may want to take a painkiller to help your body relax and ease some of the discomfort. You can ask your partner to give you a massage, or take a hot bath together.
- Set time aside to be intimate. You will need time to relax, get in the moment, pay attention to your body, and to reconnect with your partner.
- Discuss alternatives to vaginal intercourse and use this opportunity to experiment with your partner.
More
By Iris Farrou
01 Sep, 2023
Lifestyle Tips, Menopause, New Moms, Peri-Menopause, Peri-Menopause, Postpartum, Prevention, Women's Health
abdominal, Childbirth, constipation, dysfunction, floor, obesity, Pain, painful sex, pelvic, Physical Therapy, pilates, Pregnancy, pregnant, PT, tailbone, weakened pelvic floor, Why is sex painful

When we hear about pelvic floor exercises, we often associate them with either older women, or pregnant women/women who have just given birth. This is a common misconception–older women and new mothers may see immediate benefits when engaging in pelvic floor PT, but everyone can benefit from it.
No matter your age or overall physical health, if you were assigned female at birth, knowledge is power when it comes to knowing what your pelvic floor looks like, and what it does:
- Imagine your pelvic floor as a hammock of support consisting of muscles, tendons, ligaments, nerves, and connective tissue. This hammock is between the tailbone and the pubic bone.
- First and foremost, your pelvic floor supports the bowels, bladder, uterus, and vagina; there are also muscular bands that pass through the pelvic floor that encircle the urethra, vagina and anus.
- All this, when it functions properly, plays a key role in bowel and bladder control. Your pelvic floor also helps you stabilize your pelvis and your spine, and assists with sexual function.
Who is at risk of Pelvic Floor Dysfunction?
Remember that the pelvic floor is mostly made up of muscles, and like any muscles in our body those–too–can weaken or suffer damage and lead to pelvic floor dysfunction. People who have experienced pregnancy, childbirth, chronic constipation, or obesity may be at higher risk as their pelvic floor has, and does, work harder to support their normal bodily functions and the bowels/bladder.
Some of the symptoms of pelvic floor dysfunction may include pain during intercourse, bladder pain, bowel or urinary incontinence, frequent urination, persisting pubic, tailbone, or lower abdominal pain, and constipation–to name a few. More serious issues may include pelvic organ prolapse: bowel prolapse, prolapsed uterus, and even endometriosis.
How can Physical Therapy Help?
Physical therapists are not just experts who help you walk better after an injury, they are medical experts in the functions of muscles, joints, and nerves, and have an in-depth and holistic understanding of human health. Just like any medical field, PTs have areas of expertise and you may want to work with someone who is trained on pelvic floor functions.
A PT will assess your whole body after consulting with you, not just the problem or painful areas. Your medical history, symptoms, and needs will of course be taken into account to create an individualized plan for your pelvic floor health. The exercises will, and should, be done with the physical therapist–unless they assign you specific exercises to do at home. Since our pelvic floor is basically holding everything in our body together, the center so to speak, don’t be surprised if some exercises are not directly working on the pelvic area; ask your PT to explain why they are assigning you an exercise, and how it will help you. Some soreness or aches are normal after your PT sessions, but this is not a “no pain, no gain” situation: at no point during PT should you feel acute pain or strain on your muscles/ligaments.
And for this subject, the saying “the sooner, the better” cannot be emphasized enough: do not wait until you’re older, pregnant, or have any painful symptoms to get started on strengthening your pelvic floor.
More
By Iris Farrou
18 Aug, 2023
Childhood Health, Early Childhood Education, Fatherhood, Lifestyle Tips, Mental Health, New Moms, Parenting, Toddler Health, Young adults & teens
Abuse, Accident, ACE, Childhood Illness, Childhood Trauma, Children, Community, Divorce, Family Dynamic, Financial Stress, Grieving, Kids, Mental Health, Neglect, Nightmares, Pediatric, Pediatric Mental Health Care, PTSD, Teenager, Toddler Trauma, Trauma, Traumatic Childhood Experiences, Violence, Witness, Witnessing

When we’re getting ready to start a new family, we may find ourselves reflecting on our own childhood experiences, and comparing with our partner how each person grew up– perhaps the goal of this introspection is to create a new family that is healthy, happy, and flourishes with good communication. If you are in the process of family planning, you may want to take into account ACEs: Adverse Childhood Experiences.
What are they?
Adverse Childhood Experiences are traumatic events children experience between the ages of 0-17. These have long lasting effects, may lead to chronic health conditions, and people address them well into adulthood. It is important to remember that ACEs affect a child’s brain, and how they experience the world.
ACEs are quite common, with 60-80% of US adults reporting they have had at least one adverse childhood experience up until age 17, and 1 in 6 US adults saying they’ve had four or more. The most potentially traumatic ACEs can include experiencing violence, abuse, or neglect in the home, neighborhood, or school, witnessing violence in the community or otherwise living in a dangerous environment (war zone, poverty stricken areas, etc.), going through a natural disaster, witnessing serious injuries or the death of another person, losing a loved one or experiencing parental loss due to separation. However, this is by no means an exhaustive list of possible ACEs: any event that may cause trauma and long-term stress can be classified as an adverse childhood experience that adversely affects a person as an adult.
How do I know if my child has had an ACE?
The effects of a traumatic or stressful event may not be immediately visible, or take place soon after the traumatic event has occurred. If your child confides something in you that would be traumatic, then that is a clear indication of an event that would warrant immediate support–with the assistance of a mental health professional who specializes in children or teenagers.
Additionally, if you are going through something as a family, such as a divorce, death, fatal accident or illness, natural disaster, poverty, community violence, unemployment, housing and/or financial insecurity, you may want to address those events as potentially traumatic for your child. We cannot always correct or control life’s adversities, but we can recognize them for what they are and present this as a starting point to healing. If you recognize, as a family, that an event has been traumatic then this shows to your child that it’s ok for things to not be “normal”–that it’s part of life, and that our reactions or daily life will change when something happens.
If there is an event or experience that you do not know about, once your child has had time to process the experience you may start noticing signs of trauma that could include, but are not limited to: difficulty sleeping or having nightmares, wetting the bed, changes to their mood, fear of other people, difficulties in school, avoiding situations, events, or people (these may be directly associated with the traumatic event), as well as difficulty showing affection towards family and friends–especially if this is a change from their usual behavior.
How can we avoid ACEs?
The unfortunate truth is that we cannot completely eliminate ACEs, as much as we may want to. What we can do, however, is raise awareness about them so that we can all start thinking differently about childhood trauma. Historically disadvantaged populations are more susceptible to trauma, but that does not mean that everyone else is excluded. The causes may be societal, historical, natural forces, or people, but each one of us can help lessen the blow of an ACE: whether you are a parent, friend, caregiver, teacher, or neighbor. Raising awareness of ACEs means switching the focus from individual responsibility to community solutions: we can all help prevent ACEs, and help children develop strong coping mechanisms. It is important to reduce the stigma associated with parents who struggle to provide a safe environment for their children, and seek community and/or government support to do so. It is also important to remember that any one of us can promote safe, stable, and nurturing environments where children are present.
https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/aces/fastfact.html
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/24875-adverse-childhood-experiences-ace
More
By Iris Farrou
15 Aug, 2023
Diet & Exercise, Health Conditions and Pregnancy, Heart health, Lifestyle Tips, New Moms, Parenting, Pregnancy, Prevention, Women's Health, Your baby's health
Can I use antiperspirant while pregnant, Dehydration prevention, Diet during hot summer, Dizziness, Effects of overheating on pregnancy, Exercise During Pregnancy, Fainting Prevention, high temperatures, Hot Flashes during Pregnancy, How to stay hydrated while pregnant, Overheated, Overheating while Pregnant, Pregnancy, pregnant, Protecting my baby in the heat, Regulate Body Temperature

In some parts of the country the weather is starting to cool down at this time of year, but there are still areas being affected by heatwaves. Even if you’re not in the Midwest, the South, or any other part of the US where heat persists well into September, keep in mind that bigger cities suffer higher temperatures regardless. When you’re pregnant, you have an increased amount of blood in your body, which can make you feel hotter all the time. If you combine that with the summer heat, things can get really uncomfortable…
It’s a good idea to always be aware of the risks that come with a summer pregnancy:
- You are more likely to become overheated, and suffer from dizziness, nausea, headaches, or even muscle cramps.
- With that being said, keep in mind that the chances of fainting, or losing your step and falling, are higher: this could result in a more serious injury and endanger your baby’s health–even bringing on early labor or placental abruption.
- Dehydration is one of the risks associated with overheating. If your temperature is consistently above 101 degrees, you should be seeing your doctor. High fever– especially in the first trimester–has been shown to impact fetal development, particularly the fetal heart structure and neural tube defects.
- If you work outdoors, if your job requires manual labor, if you are working in a building that’s not climate controlled, or if you work in a commercial kitchen, you should know you are at higher risk of overheating while pregnant.
Though being pregnant is not the same experience for everyone, and not all people have the same advantages, opportunities, and support from family and friends during their term, the following steps are recommended so as to keep you and your baby safe:
- Since you are liable to overheat when pregnant, try to stay out of the heat as much as possible–especially if the outside temperature is higher than 90 degrees.
- Know that if your body temperature is higher than 102 degrees for more than 10 minutes, that puts you at a higher risk for heatstroke.
- Swelling and pregnancy go hand in hand, and in the summer heat this may get worse. Try to elevate your feet as much as you can, and stretch often. If you can, avoid standing for long periods of time.
- Your body is working for two, so with a higher blood volume, you will be sweating more. That’s your body trying to keep you cool: drink lots of water to avoid dehydration, and try to wear clothes that allow heat to escape.
- Underarm antiperspirant is not your friend: you need to allow your body to regulate its temperature, so you don’t want to trap heat in you. Try to wear light, breathable fabrics that help you cool down, and always use sunscreen to protect your skin from overheating.
- If you are exercising, it is best to stay inside and use AC– it is the best thing you can do for your safety to be in climate controlled environments, drink as much water as possible, and cool down every chance you get.
- Avoid the sun, avoid high sodium foods, and avoid all other drinks but water: non-alcoholic cocktails or other drinks have sugar and other ingredients that are not helping your cause. Water should be your beverage of choice.
Always trust your instincts when it comes to how you are feeling, and always listen to your body: even if the environment is seemingly cool and safe, if you feel that something is not right, follow your gut and seek medical attention.
https://www.heart.org/en/news/2019/07/01/summer-heat-brings-special-health-risks-for-pregnant-women
https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/repro/heat.html
https://www.unitypoint.org/news-and-articles/10-things-no-one-expects-during-a-summer-pregnancy
More
By Iris Farrou
27 Jul, 2023
Childhood Health, Fatherhood, Lifestyle Tips, New Moms, Parenting, Postpartum, Toddler Health, Your baby's health
are strollers too hot in the summer, Baby, Baby Safety in Summer, how do I keep my newborn safe in the sun, How to keep my baby from overheating, is central AC safe for my baby, keep my baby cool, keep my infant cool, new dads, new mom advice, new moms, newborn body temperature regulation, Toddler, toddler overheating, what clothing is best for baby in hot weather, what time of day is best to go outside during summer with newborn
 If you’re spending your first summer with your baby, there are a few things to keep in mind about newborn babies and the summer heat so everyone can remain safe and have an enjoyable summer. Depending on which part of the US you live in or are visiting this summer, keep in mind that the heat may continue into the fall months–or it may be humid heat rather than scorching sun. Either way, the key information to remember is that babies cannot regulate their own body temperatures– older children and adults are able to do so, but babies need extra assistance and protection.
If you’re spending your first summer with your baby, there are a few things to keep in mind about newborn babies and the summer heat so everyone can remain safe and have an enjoyable summer. Depending on which part of the US you live in or are visiting this summer, keep in mind that the heat may continue into the fall months–or it may be humid heat rather than scorching sun. Either way, the key information to remember is that babies cannot regulate their own body temperatures– older children and adults are able to do so, but babies need extra assistance and protection.
- Overheating is very risky for newborn babies: if you are hot, then your baby is definitely hot as well. It is not unusual or “wrong” to keep babies in either a light onesie or only a diaper.
- Keep the temperature cool: if you have a central AC or a window AC unit and can afford to keep it running to keep the temperature lower than 77F degrees, that is ideal for a baby. Utilizing box fans on your windows for air circulation, as well as ceiling fans, is another method to ensure your baby stays cool.
- Help them sleep comfortably: especially when sleeping, your baby can be only in a diaper or swaddled using very thin, lightweight and breathable material. If you are not using central AC, make sure there is a fan in the room where your baby is sleeping–preferably not pointed directly at them, though.
- Proper hydration: you know that’s true for people of all ages, and the same goes for babies. If you notice infrequent urination or crying without tears, these are signs that dehydration has already occurred. Your instinct may be to give your newborn baby water, but that is a big NO in this case; their bodies cannot process water. Breastfeeding or milk formula in smaller and more frequent doses are a better solution. If your baby is already eating other foods, try to use more hydrating foods in their diet and provide more frequent–but still smaller–meals.
If the outside temperature is above 90 degrees, or 84ish with humidity, this is when your newborn, toddlers, or young children should NOT be outside, especially no more than 15 minutes if you absolutely have to be out. Try to not stay in the heat for too long, and seek shelter in air-conditioned spaces.
If you are using a stroller, keep in mind that it may not be the best idea to go for a walk in the heat—however, you should choose a stroller with a large canopy for extra protection for the warmer months. Avoid going outside in peak heat times of 10am-2pm, and dress your baby in breathable cotton clothing, preferably loose, that covers their skin as much as possible. Wide hats and sunglasses do look adorable on babies, and are also very much necessary.
https://www.michiganmedicine.org/health-lab/how-protect-your-baby-dangers-hot-weather
https://www.whattoexpect.com/first-year/health-and-safety/how-to-protect-children-from-extreme-heat/
More
By Iris Farrou
21 Jul, 2023
Diet & Exercise, Heart health, Lifestyle Tips, Prevention, Women's Health
Best Foods for High Blood Pressure, Foods to Lower Cholesterol, Good Cholesterol, Healthy Diet, heart health, Heart Health Diet, How do I lower my cholesterol, LDL, Low Cholesterol Substitutes, Lower Cholesterol Foods, Meal Prep, What can't I eat with high cholesterol
 We hear the phrase “high cholesterol” many times, especially as we get older, but what does that really mean? Why are some people more prone to it than others? Cholesterol is a fat-like substance that the human body needs–in healthy amounts. Lipoproteins in our blood carry cholesterol, and when the situation gets a little out of hand high levels of bad cholesterol in our bodies cause fatty deposits in our blood vessels–this in turn can heighten the risk of a heart attack or a stroke.
We hear the phrase “high cholesterol” many times, especially as we get older, but what does that really mean? Why are some people more prone to it than others? Cholesterol is a fat-like substance that the human body needs–in healthy amounts. Lipoproteins in our blood carry cholesterol, and when the situation gets a little out of hand high levels of bad cholesterol in our bodies cause fatty deposits in our blood vessels–this in turn can heighten the risk of a heart attack or a stroke.
What to Cut Off
An unhealthy diet can contribute to developing bad cholesterol and/or the health issues that come with it; fast food, fried food, processed diets, saturated fats and trans fats are not friendly if you are trying to keep your cholesterol levels low. Saturated fats can be found in full-fat dairy products, as well as meat and butter. So, you may have to think twice about grabbing that delicious cheese tray from the store, cooking with butter, or consuming a lot of meat. Trans fats are often found in margarines and store-bought cookies and cakes–tempting, aren’t they? Not for your goal of lowering cholesterol!
Eliminating these products will help you lessen the bad cholesterol your lipoproteins carry. It’s not always easy to make diet changes, especially when your “comfort food” helps you deal with the stress of health issues, so it’s completely understandable that this situation may be a real pickle… (and no, you unfortunately should not have pickles either)
What to Add
The #1 goal when it comes to lessening cholesterol levels is to help your body absorb it into your bloodstream so as to avoid fatty deposits or clogged blood vessels. Foods with soluble fiber are particularly skilled in helping you get the “good kind” of cholesterol– oatmeal, oat bran, and high-fiber foods like fruit (eg. bananas and berries) are a great start!
Not this may sound contradictory to the discussion around “fats,” but there are good fats and bad fats. Margarine, saturated fats, and trans fats are a no-go. But, fatty acids are on your side: they can reduce triglycerides, which is another type of fat found in our blood, and help your body retain the good kind of cholesterol. Omega-3 fatty acids can be found in mackerel, herring, tuna, salmon, and trout– their fresh versions! For better results, it is recommended that you bake or grill the fish.
Almonds, walnuts, and avocados are also foods that can improve blood cholesterol and have been found to reduce the risk of heart attack. Keep in mind that nuts are high in calories so a handful goes a long way. Avocados are the good kind of fat– the opposite of saturated fat, and they are also high in nutrients and fiber. However, you can’t eat them in guacamole with dangerous chips: add plain avocado to your salads or your breakfast, or try it as a side dish.
What to Replace
Similar to fatty acids, olive oil–and especially extra virgin olive oil–can be really successful in ensuring the good type of cholesterol is absorbed by your body. You can replace pretty much any use of butter with olive oil–the difference in taste will be minimal, and the health improvements will be tremendous.
Another thing you will need to replace, and that’s not necessarily in the kitchen, is your general stance on everyday life. Lack of physical activity is a very high risk factor for heart disease–it doesn’t matter where you are on your journey or if your body can only do so much; you have to start from where you are and build up to your body’s capacity of exercising regularly. This will also slowly start to help you with maintaining a healthy weight and lessen your chances of developing heart disease, high blood pressure, or other serious health problems.
Even if you are young and healthy, and we do hope you are, remember that knowledge is always power; check your cholesterol levels during regular blood tests and doctor visits, and keep an eye on your family history for cholesterol-related diseases.
More
 If you have a family history of osteoporosis or are postmenopausal and suspect osteoporosis will affect your quality of life, then it may be time to take a closer look at what this “silent disease” i, how you can prevent it from taking control of your life, and the medical technology available to help you know your body.
If you have a family history of osteoporosis or are postmenopausal and suspect osteoporosis will affect your quality of life, then it may be time to take a closer look at what this “silent disease” i, how you can prevent it from taking control of your life, and the medical technology available to help you know your body.